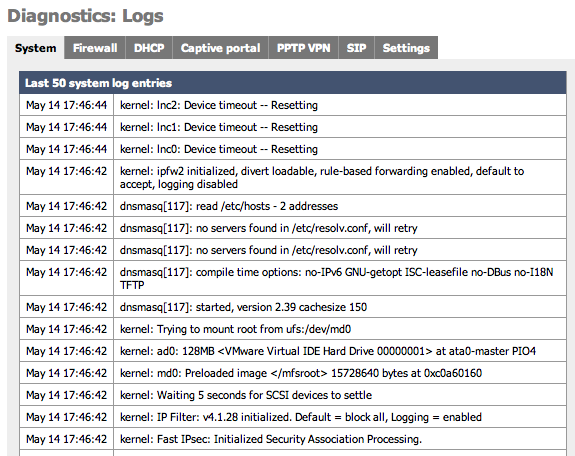
System logs are available for the following services:
System logs
Firewall
DHCP
Captive Portal
PPTP VPN
SIP (in firmware 1.3 and higher)
Caution
The logs are limited to available RAM and are erased after a reboot. To store logs permanently you should enable the use of a remote syslog server on the Diagnostic Log Settings page.
System log (often called syslog) settings can also be configured on this page by clicking on the Settings tab. When sending Syslog to a remote server m0n0wall sends UDP datagrams to port 514 on the specified remote syslog server. Be sure to set syslogd on the remote server to accept syslog messages from m0n0wall and to not block the traffic in any intervening firewalls.
Caution
Because of the detailed information that these messages can contain about your network it is highly recommended to not send syslog messages over the Internet unless they are inside an encrypted tunnel like PPTP or IPSec.
Table 4.4. Log Settings Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Show log entries in reverse order | optionally show logs with the newest on top |
| Number of log entries | how many log entries to keep |
| Log packets blocked by the default rule | Hint: packets that are blocked by the implicit default block rule will not be logged anymore if you uncheck this option. Per-rule logging options are not affected. |
| Show raw filter logs | Hint: If this is checked, filter logs are shown as generated by the packet filter, without any formatting. This will reveal more detailed information. |
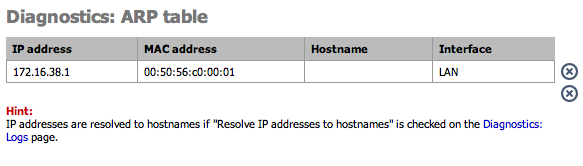
| Resolve IP addresses to hostnames | Hint: If this is checked, IP addresses in firewall logs are resolved to real hostnames where possible. Warning: This can cause a huge delay in loading the firewall log page! This can often be done by a remote syslog server. |
| Enable syslog'ing to remote syslog server | Activate the use of a remote syslog server to store log messages outside of the m0n0wall device. |
| Remote syslog server | The IP address of remote syslog server and which events should be sent to the syslog server. |
It is recommended that you log your m0n0wall to a remote syslog server for diagnostics and forensic purposes. There are a number of free tools receive and store syslog messages for you on Windows, Mac, and Unix based systems. These software packages also offer additional features such as automatically sending pages, emails or SMS messages as well as running software or commands based on the messages that are received. Some software packages are listed here.
Some operating systems that are by default using syslog messages, such as MacOSX, may have default configurations that limit reception of syslog messages from external sources. If you hav problems receiving messages verify that your syslog server software can receive external messages.
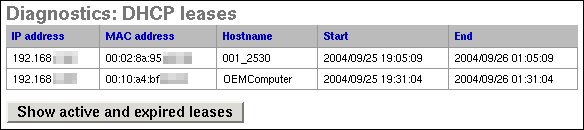
This screen can be used to view your active and/or expired DHCP leases. Clicking the button on this screen will switch between showing only active leases and showing both active and expired leases.
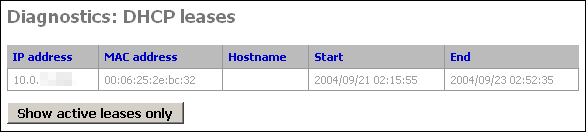
Expired DHCP leases show up in gray text, while active ones are black. (this screenshot from a system with only expired leases)
IPsec maintains two databases with connection details.
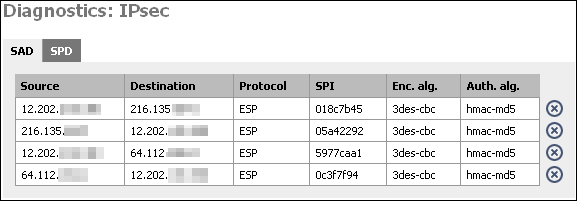
Security Association Database
First is the Security Association Database (SAD). This database maintains a list of all current IPsec Security Associations (SA's).
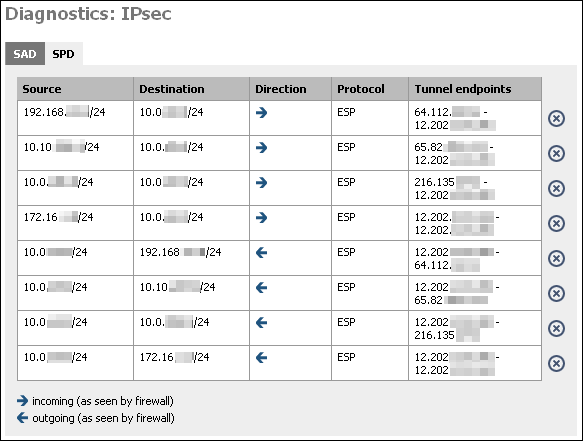
Security Policy Database
Second is the Security Policy Database (SPD). This database maintains a list of all the IPsec policies on the system. You will have two SPD entries for each IPsec VPN connection you have configured, regardless of whether the connection is up. This database tells the system what traffic will pass over VPN, and specifically which tunnel it traverses.
Table 4.5. The two entries for each VPN connection are as follows:
| Source | Destination | Direction | Protocol | Tunnel Endpoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| local IP subnet for VPN connection | remote IP subnet for VPN connection | ESP or AH | Public IP address of local m0n0wall - Public IP address of remote endpoint | |
| remote IP subnet for VPN connection | local IP subnet for VPN connection | ESP or AH | Public IP address of remote endpoint - Public IP address of local m0n0wall |
At this screen, you will see two entries for each IPsec connection that has been successfully negotiated. One from the local public IP to the remote endpoint's public IP, and one in the opposite direction. This indicates that IPsec negotiations were successful, and that traffic should now be passing your VPN connection if everything else is configured appropriately.
By clicking on the X, you can delete the SA. m0n0wall will attempt to recreate it after deleting it. If you have a VPN connection with duplicate SA's (more than one from same src to same dst) and the connection has gone down, delete all the SA's associated with the connection. It should renegotiate and come back up within a few seconds.
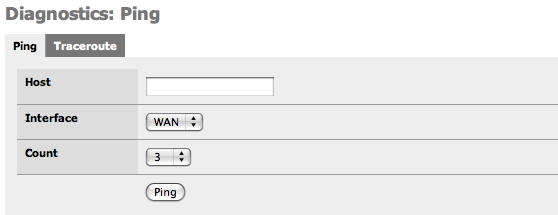
This screen gives you a GUI to ping (send ICMP echo request) from the m0n0wall. Fill in the IP address or hostname of the machine to ping, choose the number of pings in the count drop down, and click the Ping button.
Note
The m0n0wall ping screen cannot ping over VPN connections for the same reason SNMP does not work over VPN out of the box. See this FAQ entry for more information. So do not use this screen as an indicator of whether your VPN is working.
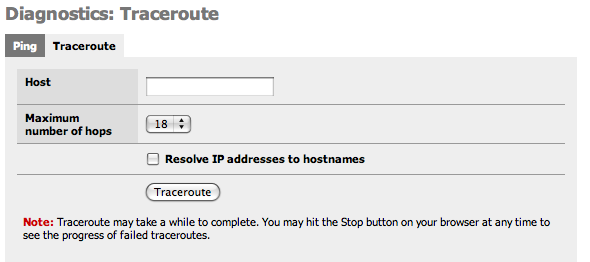
This screen gives you a GUI to traceroute from the m0n0wall. Fill in the IP address or hostname of the machine whose route you want to trace, choose the maximum number of hops in the drop down, and click the Traceroute button.
Note
The m0n0wall ping screen cannot make traceroutes over VPN connections for the same reason SNMP does not work over VPN out of the box. See this FAQ entry for more information. So do not use this screen as an indicator of whether your VPN is working.
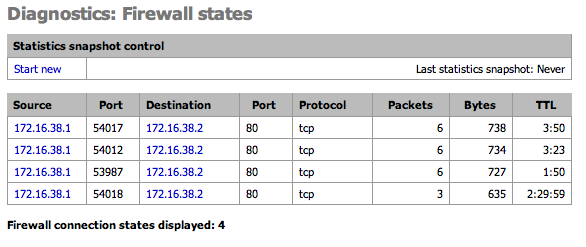
This page shows the current Firewall state table. Optionally take a snapshot of the state stable and compare it to the current table.
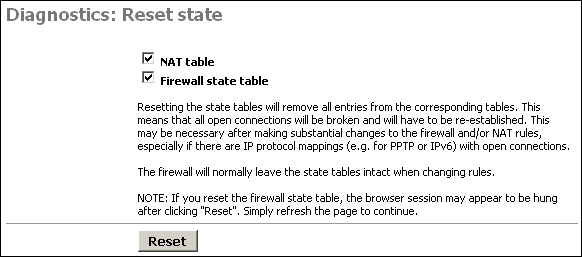
This screen allows you to reset the state tables on your m0n0wall for the NAT and firewall state tables.
Just check the boxes for the table(s) you want to clear, and click the Reset button.
Resetting the state tables will remove all entries from the corresponding tables. This means that all open connections will be broken and will have to be re-established. This may be necessary after making substantial changes to the firewall and/or NAT rules, especially if there are IP protocol mappings (e.g. for PPTP or IPv6) with open connections.
The firewall will normally leave the state tables intact when changing rules.
NOTE: If you reset the firewall state table, the browser session may appear to be hung after clicking "Reset". Simply refresh the page to continue.
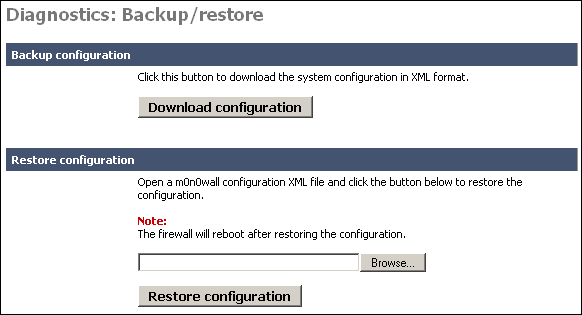
This screen allows you to backup your existing configuration, or restore a previous backup file. These files are text based XML files.
To backup your m0n0wall, click the "Download configuration" button. This will download a file called (by default) config.xml.
If you ever need to restore a previous backup file, go to this page, and under the "Restore configuration" section, click Browse. Locate the config.xml file you backed up above.

Clicking Yes on this page will reset m0n0wall to the default out of the box configuration options and clear any configuration you have done on the device.
If all else fails when trying to configure something on your m0n0wall, sometimes it is easiest to start over from scratch on the entire configuration. In that instance, use this feature to reload the default settings.

Click Yes on this page to reboot the system.
As a general rule of thumb in m0n0wall and FreeBSD in general, rebooting probably isn't going to fix any problems you are having. But it is worth a shot in many circumstances.
Unlike so many systems, rebooting isn't a suggested maintenance procedure on m0n0wall. There is no need to reboot the system unless you have a specific reason for doing so.