- ACL
Access Control List.
- AH
-
Authentication Header. The Authentication Header is used to provide connectionless integrity and data origin authentication for IP datagrams. Note: AH will not work through NAT, so if you are placing your m0n0wall behind another firewall or layer 2 router that is performing NAT AH will not work. Unless you really have a reason, use ESP.
- Broadcast Domain
-
A broadcast domain is the portion of a network sharing the same layer two network segment. In a network with a single switch, the broadcast domain is that entire switch. In a network with multiple switches interconnected by crossover cables without the use of VLAN's, the broadcast domain includes all of those switches.
A single broadcast domain can contain more than one IP subnet, however that is generally not considered good network design. IP subnets should be segregated into separate broadcast domains via the use of separate switches, or VLAN's.
- DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. A protocol to automate the assignment of IP addresses and related information on a network.
- DMZ
-
A DMZ, or DeMilitarized Zone, is a segment of your network specifically for publicly-accessible servers. If you are most familiar with residential-class routers like Linksys and similar, these devices generally incorrectly refer to inbound NAT (opening ports from the internet to your LAN) as "DMZ" functionality.
A true DMZ resides on a separate broadcast domain from the LAN, typically on a separate switch using a third interface on the firewall. VLAN's can also be used, but to eliminate the potential of a switch misconfiguration exposing your LAN to your DMZ and the potential effects of VLAN hopping attacks, this is not recommended.
The main purpose of a DMZ is to segregate Internet-accessible servers from the LAN, to protect your trusted networks if a DMZ host is compromised.
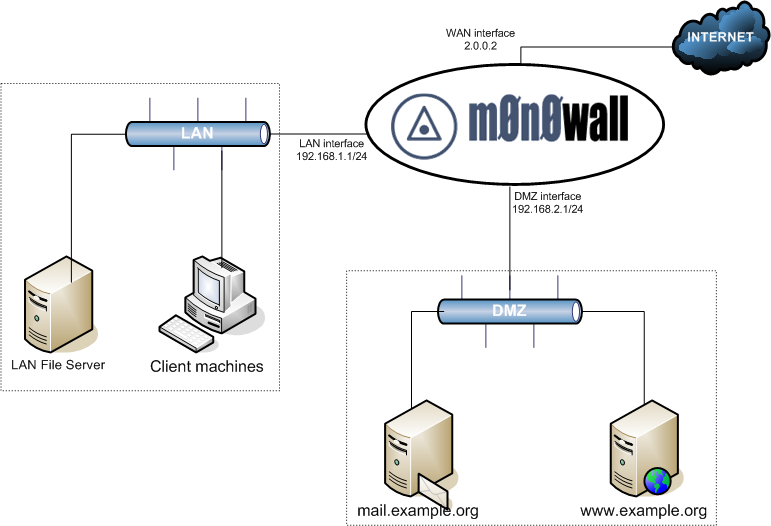
Typical DMZ Configuration. The following diagram illustrates a typical DMZ configuration.
- ESP
-
Encapsulating Security Payload. Encrypts and / or authenticates everything above the IPsec layer. ESP, most agree, renders AH completely unnecessary.
See Also http://www.networksorcery.com/enp/protocol/esp.htm.
- FQDN
Fully Qualified Domain Name. The host name of a computer, including it's complete domain name, such as www.m0n0.ch.
- ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol. A protocol, layered on top of IP, used to send control messages between computers, such as ping.
- IP
-
Internet Protocol. The protocol used to send packets across the Internet at layer three.
- IPsec
-
Secure transmission over IP. IPsec is an extension of the IP protocol used for encryption and authentication. Encryption occurs at the transport layer of the OSI model, the application doesn't have to support encryption for the encryption process to work. Therefore, all network traffic generated by applications can be encrypted regardless of the application
See Also http://www.netbsd.org/Documentation/network/ipsec/.
- LAN
-
Local Area Network. A network that typically includes computers which are physically close, such as in one office, usually connected with hubs and switches rather than routers.
- MX Records
MX records are DNS records that enable mail servers to find the mail servers for another domain when sending internet email. When a mail server needs to send an email to example.com, it performs a DNS lookup of the MX record for the domain, and sends the email to the resulting host.
- NIC
Network Interface Card. A.k.a. network card, or Ethernet card.
- NAT
Network Address Translation. A technique whereby IP traffic from multiple IP addresses behind a firewall are made to look to the outside as if they all come from a single IP address.
- OSI
- Proxy ARP
-
Proxy ARP is a technique for using the ARP protocol to provide an ad hoc routing mechanism.
A multi-port networking device (e.g. a router, firewall, etc.) implementing Proxy ARP will respond to ARP requests on one interface as being responsible for addresses of device addresses on another interface. The device can then receive and forward packets addressed to the other devices. (adapted from wikipedia.org)
In m0n0wall, Proxy ARP can be used for 1:1, advanced outbound, and server NAT , amongst other potential uses.
- PPP
Point to Point Protocol.
- PPTP
Point to Point Tunneling Protocol.
- Racoon
-
A key management daemon. The magic behind the VPN power of m0n0wall.
See Also http://www.kame.net/racoon/.
- TCP
Transmission Control Protocol. A protocol, layered on top of IP, that handles connections and reliable delivery.
- VLAN
Virtual Local Area Network. VLAN's are a common function of higher end switches. They allow segregation of ports on the switch into separate broadcast domains. This is generally done for security or performance reasons. In very large networks, the amount of broadcast traffic on the wire can inhibit the performance of the entire network. Segregating the network into multiple IP subnets and using VLAN's to separate the broadcast domain
- VPN
Virtual Private Network. A connection between two or more machines or networks where the data travels over an insecure network (typically the Internet), but is encrypted to prevent eavesdropping, and packaged on either end in order to make the two ends appear to be on a WAN.
- WOL - Wake on LAN
-
Wake on LAN is a capability in some network cards permitting powering on the system over the network with a specially crafted "Magic Packet".
Generally a WOL cable must be attached from the NIC to the motherboard of the system. Most NIC's built into the motherboard have this support built in. You must enable WOL in the BIOS of the machine. This is generally off by default.
- WAN
-
Wide Area Network. A network that spans a large area, typically including routers, gateways, and many different IP address groups.
In the context of firewalls, the WAN interface is the one directly connected to the Internet. In the context of corporate networks, the WAN generally refers to the network that connects all of the organization's locations onto the corporate network. Historically this was accomplished with expensive private leased lines like frame relay and similar technologies. With the low cost and widespread availability of broadband Internet connections, many organizations are switching to using VPN in lieu of leased lines. VPN provides the same functionality, though is not as reliable as leased lines and has higher latency.